This brief infographic describes the dangers of phosgene exposure. Phosgene is a potentially deadly gas that should be avoided at all costs. Phosgene gas is created when heat is applied to brake cleaner, making it a potential hazard to welders. While a dust and fume collector will not eliminate phosgene, you can take proper precautions to avoid it.
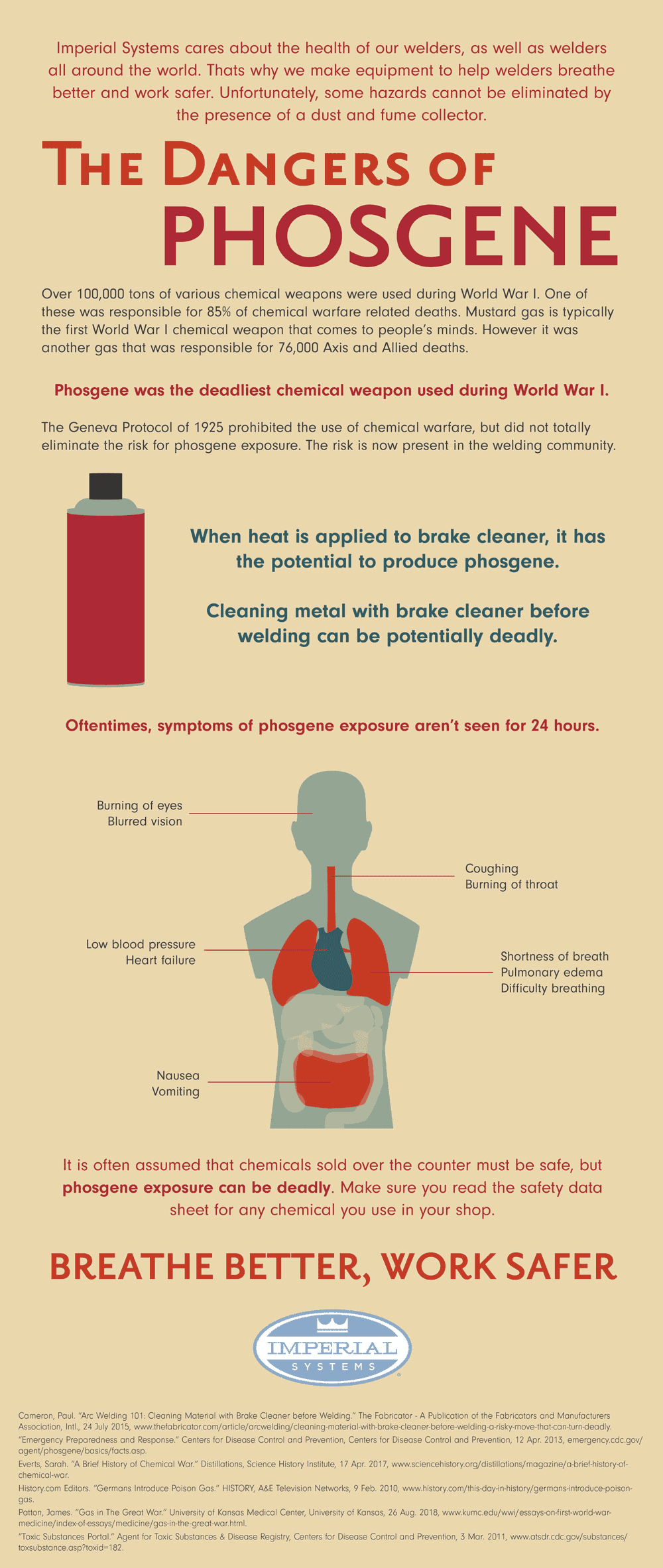
Over 100,000 tons of various chemical weapons were used during World War I. One of these was responsible for 85% of chemical warfare-related deaths. Mustard gas is typically the first World War I chemical weapon that comes to people’s minds. However, it was another gas that was responsible for 76,000 Axis and Allied deaths.
Phosgene exposure was the deadliest chemical weapon used during World War I
The Geneva Protocol of 1925 prohibited the use of chemical warfare but did not totally eliminate the risk of phosgene exposure. The risk is now present in the welding community. When heat is applied to brake cleaner, it has the potential to produce phosgene. Cleaning metal with brake cleaner before welding can be potentially deadly.
Oftentimes, symptoms of phosgene exposure are not seen for 24 hours. These include burning of the eyes and throat, blurred vision, coughing, difficulty breathing, pulmonary edema, nausea, vomiting, low blood pressure, and heart failure. It is often assumed that chemicals sold over the counter must be safe, but phosgene exposure can be deadly. Make sure you read the safety data sheet for any chemical you use in your shop.
Imperial Systems cares about the health of our welders, as well as welders all around the world. That’s why we make equipment to help welders breathe better and work safer. Unfortunately, some hazards cannot be eliminated by the presence of a dust and fume collector.
Learn more about phosgene gas in this related blog post.


